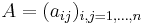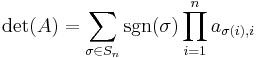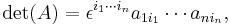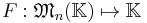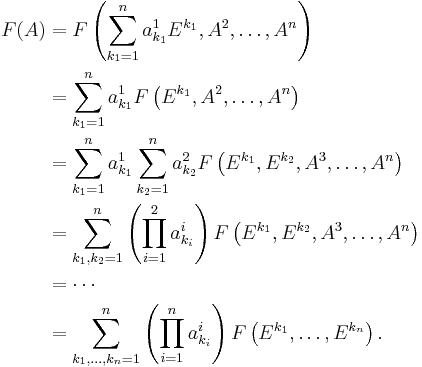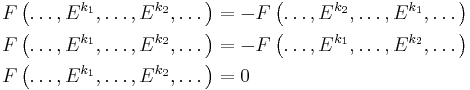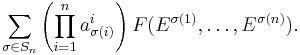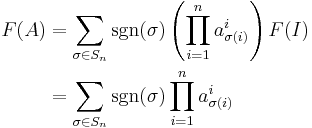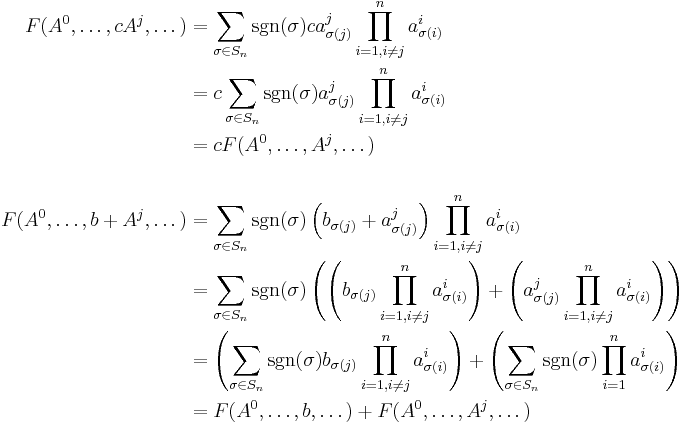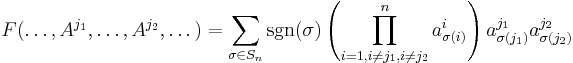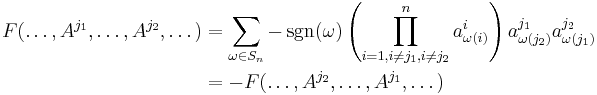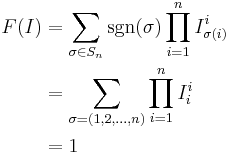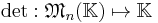Leibniz formula for determinants
In algebra, the Leibniz formula expresses the determinant of a square matrix
in terms of permutations of the matrix elements. Named in honor of Gottfried Leibniz, the formula is
for an n×n matrix, where sgn is the sign function of permutations in the permutation group Sn, which returns +1 and −1 for even and odd permutations, respectively.
Another common notation used for the formula is in terms of the Levi-Civita symbol and makes use of the Einstein summation notation, where it becomes
which may be more familiar to physicists.
Directly evaluating the Leibniz formula from the definition requires 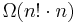 operations in general—that is, a number of operations asymptotically proportional to n factorial—because n! is the number of order-n permutations. This is impractically difficult for large n. Instead, the determinant can be evaluated in O(n3) operations by forming the LU decomposition
operations in general—that is, a number of operations asymptotically proportional to n factorial—because n! is the number of order-n permutations. This is impractically difficult for large n. Instead, the determinant can be evaluated in O(n3) operations by forming the LU decomposition 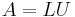 (typically via Gaussian elimination or similar methods), in which case
(typically via Gaussian elimination or similar methods), in which case 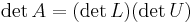 and the determinants of the triangular matrices L and U are simply the products of their diagonal entries. (In practical applications of numerical linear algebra, however, explicit computation of the determinant is rarely required.) See, for example, Trefethen and Bau (1997).
and the determinants of the triangular matrices L and U are simply the products of their diagonal entries. (In practical applications of numerical linear algebra, however, explicit computation of the determinant is rarely required.) See, for example, Trefethen and Bau (1997).
Formal statement and proof
Theorem. There exists exactly one function
which is alternate multilinear w.r.t. columns and such that 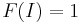 .
.
Proof.
Uniqueness: Let 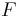 be such a function, and let
be such a function, and let 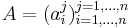 be an
be an 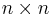 matrix. Call
matrix. Call 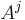 the
the 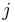 -th column of
-th column of  , i.e.
, i.e. 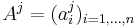 , so that
, so that 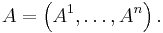
Also, let 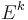 denote the
denote the 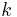 -th column vector of the identity matrix.
-th column vector of the identity matrix.
Now one writes each of the 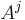 's in terms of the
's in terms of the 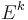 , i.e.
, i.e.
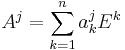 .
.
As 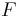 is multilinear, one has
is multilinear, one has
From alternation, it follows that if 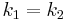 then
then
As the above sum takes into account all the possible choices of ordered  -tuples
-tuples  , and because
, and because 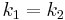 implies that F is zero, the sum can be reduced from all tuples to permutations as
implies that F is zero, the sum can be reduced from all tuples to permutations as
Because F is alternating, the columns 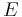 can be swapped until it becomes the identity. The sign function
can be swapped until it becomes the identity. The sign function 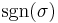 is defined to count the number of swaps necessary and account for the resulting sign change. One finally gets:
is defined to count the number of swaps necessary and account for the resulting sign change. One finally gets:
as 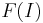 is required to be equal to
is required to be equal to 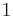 .
.
Therefore no function besides the function defined by the Leibniz Formula is a multilinear alternating function with 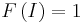 .
.
Existence: We now show that F, where F is the function defined by the Leibniz formula, has these three properties.
Now let 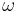 be the tuple equal to
be the tuple equal to 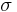 with the
with the 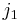 and
and 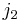 indices switched. It follows from the definition of
indices switched. It follows from the definition of 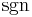 that
that 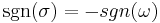 .
.
Finally, 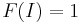 :
:
Thus the only functions which are multilinear alternating with 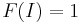 are restricted to the function defined by the Leibniz formula, and it in fact also has these three properties. Hence the determinant can be defined as the only function
are restricted to the function defined by the Leibniz formula, and it in fact also has these three properties. Hence the determinant can be defined as the only function
with these three properties.
See also
References
- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001), "Determinant", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1556080104, http://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Determinant&oldid=12692
- Lloyd N. Trefethen and David Bau, Numerical Linear Algebra (SIAM, 1997).